

Why can we relate classical physics to quantum mechanics when it comes to subatomic activity?.Which electrons shields better in an atom? 2 s or 2 p ? 3 p or 3 d?.Why do the orbitals of a hydrogen atom increase energy as follows: 1 s Which electron has higher energy level? 2 s or 2 p ? and why?.In the simplest case, every electron in an atom would feel the same amount of “pull” from the nucleus.

S average amount of density between the nucleus and the electron. Z denotes the number of protons existing in the nucleus. More distance between the charges will result in less force, and more charge will have more force of attraction or repulsion. Besides, the formula for calculating the effective nuclear charge of a single electron is as follows: Zeff Z S.
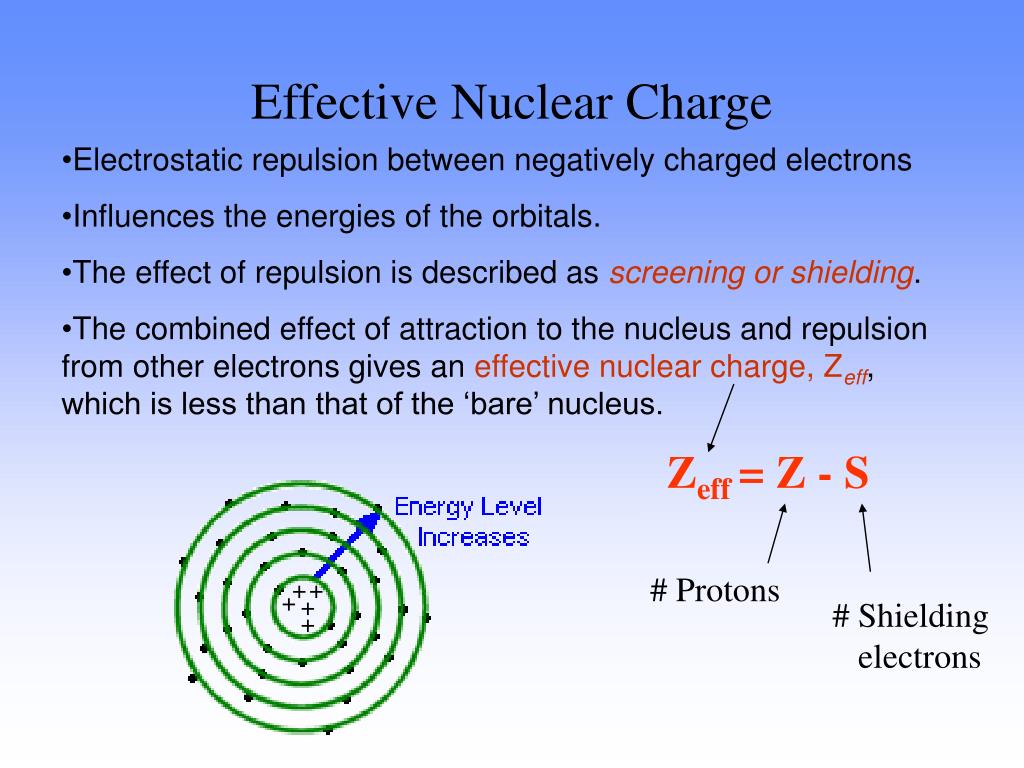
The force that an electron feels is dependent on the distance from the nearest charge (i.e., an electron, usually with bigger atoms and on the outer shells) and the amount of charge. The ability of an electron to get close to the nucleus is penetration.Ĭoulomb’s Law can be used to describe the attraction and repulsion between atomic particles. The orbital ( n) and subshell ( m l) define how close an electron can approach the nucleus. The balance between attractive and repulsive forces results in shielding. The electrons are attracted to the nucleus at the same time as electrons repel each other. IntroductionĮlectrons are negatively charged and are pulled pretty close to each other by their attraction to the positive charge of a nucleus. We can predict basic properties of elements by using shielding and penetration characteristics to assess basic trends. Penetration and shielding are two underlying principles in determining the physical and chemical properties of elements.
Effective nuclear charge of oxygen how to#
How to Calculate Effective Nuclear Charge Because of the varying charge on electrons in different orbitals, we typically refer to the effective nuclear charge, which is the effect of the nucleus experienced by the outermost electron of the atom, taking into account the shielding effect of inner electrons.
Effective nuclear charge of oxygen full#
The presence of electrons on the inner shells of an atom “shield” the outermost electron from feeling the full positive charge. This results in a varying attraction of the nucleus on the electrons surrounding the nucleus, which is known as nuclear charge. However, negatively charged electrons around the nucleus are organized into layers called orbitals which repel each other, and negate some of the positive charge of the nucleus. Electrons are attracted to the nucleus as they are negatively charged. The nucleus of an atom contains positively charged particles called protons. The net attraction on these outer electrons is known as effective nuclear charge. Electrons are attracted to the nucleus as it is positively charged, but electrons in the inner shells can negate some of the attraction of the nucleus on the outermost electrons. Nuclear charge is a measure of the ability of protons in the nucleus to attract the negative electrons in orbit around the nucleus. The equation for calculating nuclear charge is Zeff = Z - S, where Zeff is the effective nuclear charge, Z is the number of protons, and S is the number of inner electrons.ģ. You can calculate effective nuclear charge if you know the number of inner electrons and the number of protons of an atom, both which can be found either from the periodic table or from online resources. How do you calculate effective nuclear charge? Nuclear charge values have been determined for the elements. These values are recorded in encyclopedias, scientific textbooks, and scientific journal articles.Ģ. How do you find effective nuclear charge? These outer electrons are also known as valence electrons.ġ. Elements in different groups on the periodic table have different numbers of electrons in their outermost shells. These negatively charged electrons are arranged into shells which form layers surrounding the nucleus. Refresher: Atoms are composed of a nucleus, containing positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
